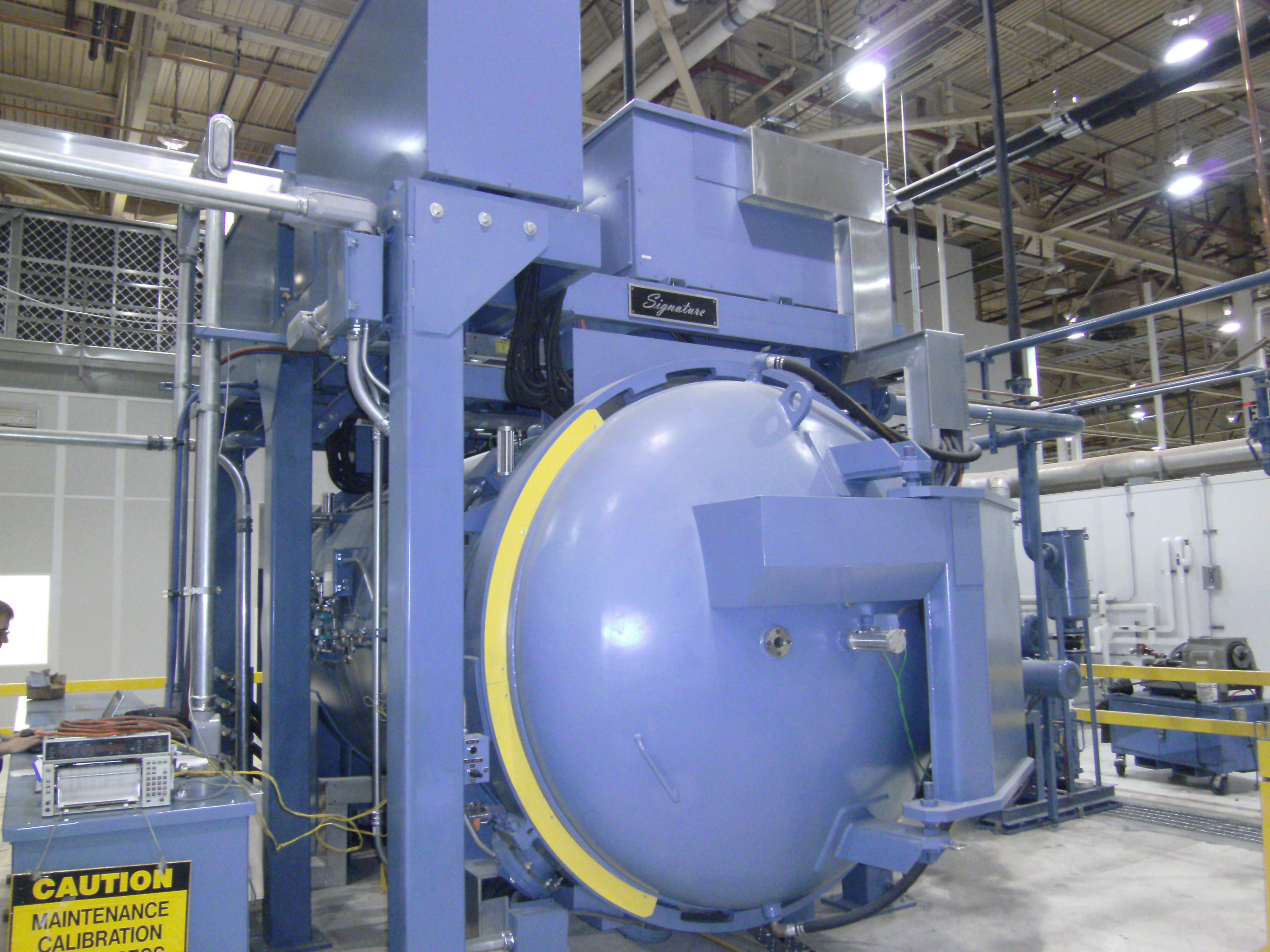
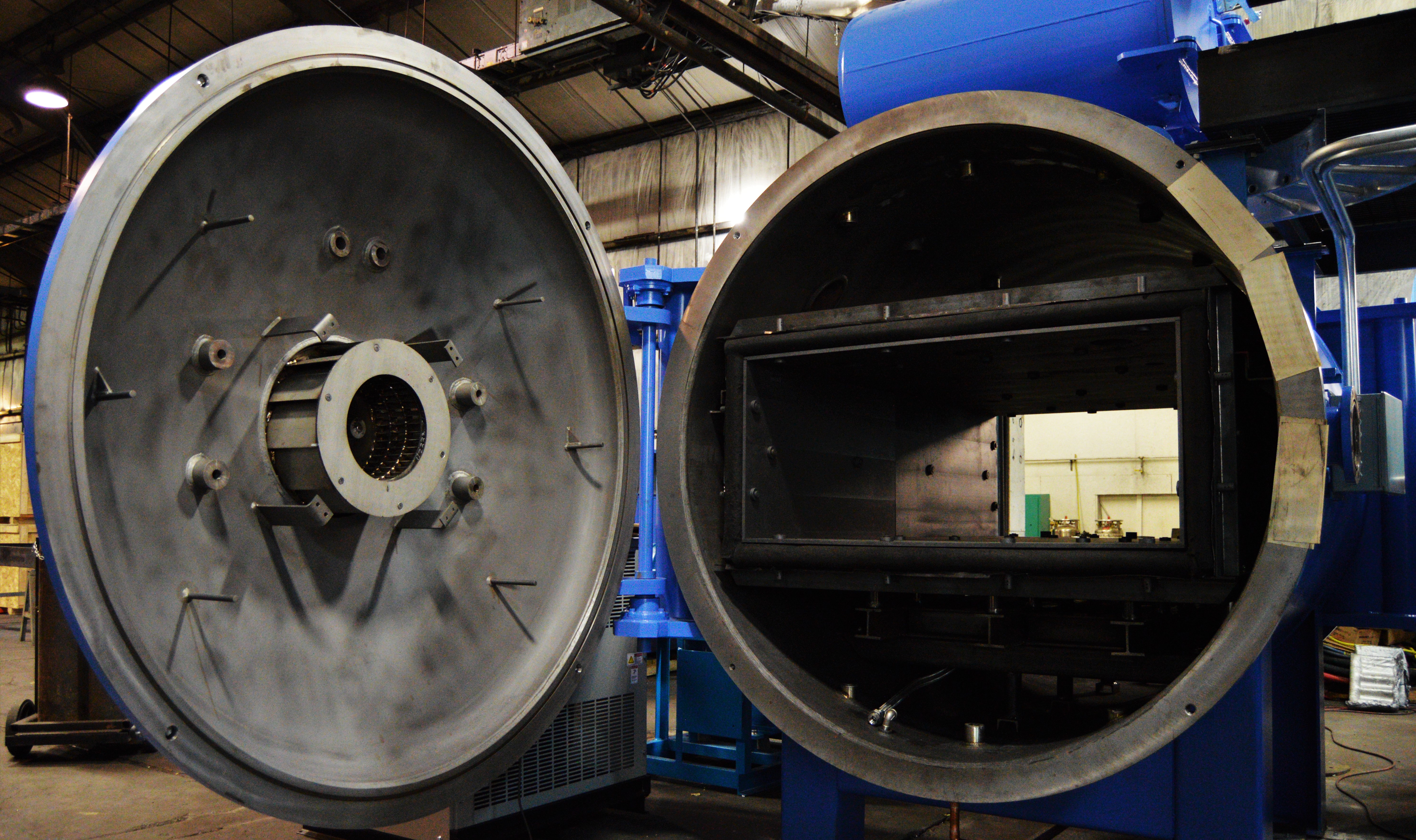
Small or complex parts are difficult to produce by casting or machining. Components that require sintering are often delicate, intricate, and easy to botch. Vacuum sintering is an efficient way to join parts with minimal waste....
Read MoreVacuum Sintering: Why Choose a Vacuum Furnace for Sintering?
Vacuum Heat Treating: Why Heat Treat in a Vacuum Furnace?
Vacuum heat treating is performed to alter the mechanical or chemical properties of a metal. In general, heat treating is meant to improve the metal's properties, including increasing material strength, durability, hardness, corrosion resistance, and more....
Read MoreThe definition of brazing is to join two or more pieces of metal by means of flowing a filler metal between the joint interfaces at a temperature below the melting point of the base metal but above 840°F....
Read MoreThe Beginner's Guide to Vacuum Aluminum Brazing (VAB)
Aluminum brazing in a vacuum furnace is considered fluxless brazing because flux is not used to remove oxides. Vacuum pumps evacuate the furnace, thereby reducing the PPM oxygen level in the brazing chamber thus inhibiting oxide formation. Magnesium is used as a getter in vacuum aluminum brazing to ...
Read MoreVacuum Brazing - Why Switch to Brazing in a Vacuum Furnace?
Vacuum brazing, and brazing in general, is an often-overlooked but highly essential process in metal joining. Its close cousins, soldering and welding, can at times overshadow this highly useful and effective joining process. Though it is often used in large-scale applications like automotive and ...
Read More
.jpg)